Original link:Metaorganisms - Non coding RNA
Non coding RNA refers to RNA that does not encode proteins, including miRNA, lncRNA, circRNA, piRNA, etc. Non coding RNA functions in many ways, interacting with proteins, DNA, and RNA to participate in various cellular activities, including gene activation and silencing, RNA splicing, modification, and editing, and protein translation.
1. miRNA: miRNA is a type of non coding single stranded RNA molecule with a length of approximately 22 nucleotides encoded by endogenous genes, which participates in post transcriptional gene expression regulation in animals and plants. Each miRNA can have multiple target genes, and several miRNAs can also regulate the same gene.
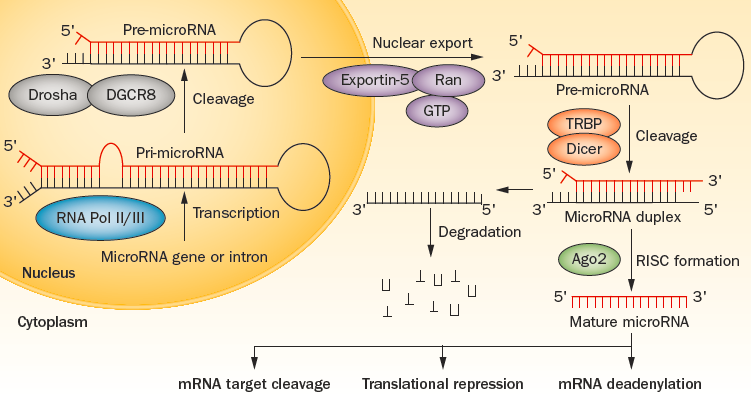
Figure 1 miRNA maturation and mode of action (Mikhailidis DP, Athyros VG. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2014 Feb; 11 (2): 72-4)
Overexpression of miRNA: Constructing miRNA precursor sequences into viral vectors, which can be used for transient transfection of cells or packaged into viruses for stable strain screening and animal level overexpression of miRNA.
MiRNA knockdown: Design a TuD RNA blocking fragment or sponge fragment targeting miRNA, and then construct the fragment into a viral vector. This vector can be directly transfected into cells for miRNA knockdown, or packaged as a lentivirus for animal level miRNA knockdown.
MiRNA target gene prediction: miRNA recognizes the 3'UTR region of target genes through base complementary pairing, and guides the silencing complex to degrade or inhibit the translation of target mRNA based on the degree of complementarity. Therefore, the 3 'UTR region of the target gene can be constructed onto a reporter gene containing luciferase, and the effect of miRNA on the target gene can be determined by comparing the changes in fluorescence values detected by miRNA overexpression or inhibitor with the reporter gene. Further determine the site of action between miRNA and the target gene 3'UTR by site directed mutagenesis of the 3'UTR region.
Common miRNA databases:
(1) MiRBase( http://www.mirbase.org ): miRbase is an online miRNA database developed by researchers at the University of Manchester, which provides a comprehensive database of published miRNA sequence data, annotations, predicted gene targets and other information, and is one of the most important public databases for storing miRNA information.
(2) Targeted Scan( http://www.targetscan.org/ )Targeted Scan predicts target genes by searching for conserved 8mer and 7mer loci that match each miRNA seed region.
(3) TarBase( http://carolina.imis.athena-innovation.gr/diana_tools/web/index.php?r=tarbasev8%2Findex )The TarBase database spent about 10 years manually collecting target genes of experimentally validated miRNAs, including those in humans, mice, fruit flies, worms, and zebrafish.
(4) MiRWalk( http://www.ma.uni-heidelberg.de/apps/zmf/mirwalk/ )MiRKalkis is a comprehensive database that provides predicted information on miRNAs from humans, mice, and rats, as well as validated binding sites located on their target genes.
2. lncRNA: lncRNA is the abbreviation for long non coding RNA, which is an RNA molecule with a length between 200-100000 nt. Most lncRNAs exhibit significant spatiotemporal expression specificity during tissue differentiation and development; The conservation of sequences is relatively low, with only about 12% of lncRNAs found in organisms other than humans.
According to the position of lncRNAs relative to protein coding genes on the genome, they can be classified into seven types: promoter associated, intronic, bidirectional, sense, antisense, 3'UTR associated, and intergenic. This positional relationship is of great help in inferring the function of lncRNAs.
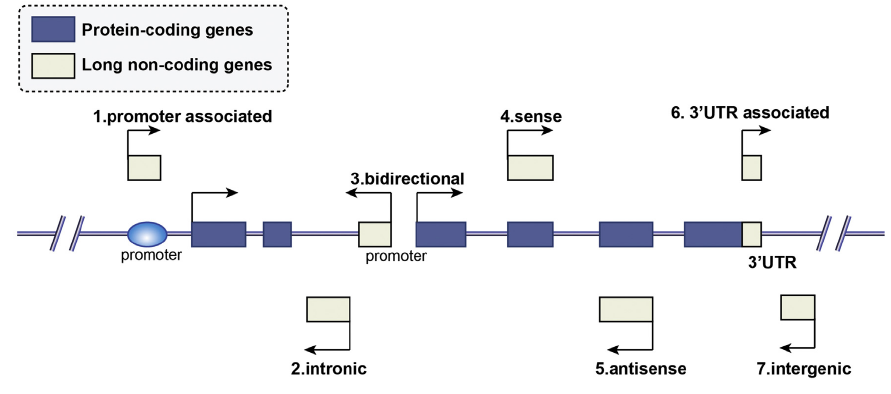
Figure 2 Classification of lncRNAs (Huang X, et al.Cancer Lett. 2018 Jan 28;413:94-101.)
Generally speaking, lncRNAs mainly regulate gene expression from the following three levels:
(1) Epigenetic regulation: lncRNAs recruit chromatin remodeling complexes to specific sites, thereby mediating the silencing of related gene expression.
(2) Transcription regulation: including the following: 1) The transcription of lncRNA can interfere with the expression of neighboring genes; 2) LncRNA can interfere with gene expression by blocking the promoter region; 3) LncRNA can interact with RNA binding proteins and localize them to gene promoter regions to regulate gene expression; 4) LncRNA can regulate the activity of transcription factors; 5) LncRNA can also regulate gene expression by modulating basic transcription factors.
(3) Post transcriptional regulation: lncRNA can regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional level by forming a double strand with mRNA.
Overexpression of lncRNA: Constructing lncRNA sequences into viral vectors, which can be used for transient transfection of cells or packaged into viruses for stable strain screening and animal level overexpression of lncRNA.
LncRNA interference: Design interference fragments targeting lncRNA and construct the fragments into viral vectors. This vector can be directly transfected into cells for lncRNA interference, or packaged as a lentivirus for animal level interference of lncRNA.
Knockout of lncRNA: Knockout of lncRNA using CRISPR/Cas9 technology. Design multiple sgRNA sequences at both ends of a certain lncRNA fragment to achieve large fragment deletion and achieve knockout effect. Construct the sgRNA sequence into a viral vector, then load the Cas9 sequence into another vector, and subsequently infect the target cells with both viruses for knockout.
Searching for lncRNA target genes: The method is similar to the miRNA dual luciferase assay described above.
3. circRNA: circRNA, also known as circular RNA, is a type of non coding RNA molecule that objectively exists in living organisms without a 5 'end cap and a 3' end poly (A) tail, and forms a circular structure through covalent bonds.
The main characteristics of circRNA are:
(1) CircRNAs are produced by special variable splicing and are abundant in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells, mainly derived from exons, with a small portion of circRNAs derived from introns present in the nucleus.
(2) The expression level has species, organization, and time specificity.
(3) CircRNA has a closed circular structure and is not easily degraded by nucleases, making it more stable than linear RNA.
(4) Has a certain degree of sequence conservation.
(5) Plays a regulatory role at the transcriptional or post transcriptional level.
(6) The vast majority of circRNAs are non coding, but there are also a few that can be translated into peptides.
CircRNAs can be divided into three categories based on their sources: exon derived circRNAs, intron derived circRNAs, and retained intron circRNAs.
The mechanism of action of circRNA:
MiRNA molecular sponge, circRNA contains a large number of miRNA binding sites and has miRNA sponge function, indirectly regulating the expression of downstream target genes of miRNA.
Regulating gene transcription, circRNA can also regulate protein function by binding to RNA binding proteins, such as inhibiting gene transcription by binding to transcription factors.
Although circRNAs belong to non coding RNAs, there are also a few circRNAs that can encode peptides and exercise regulatory functions through these peptides.
Overexpression of circRNA: Similar to the lncRNA steps mentioned above, but due to the impact of loop formation efficiency, overexpression of circRNA is more difficult compared to overexpression of ordinary genes.
CircRNA interference: the same steps as the lncRNA method mentioned above.
CircRNA knockout: the same steps as the lncRNA method mentioned above.
CircRNA target gene search: using the same miRNA and lncRNA dual luciferase detection method as described above.
Our advantages:
1) Rich project experience and high success rate;
2) Price discounts, enjoy discounts;
3) Short experimental period;
4) Comprehensive after-sales service.
The services we can provide:
service content | Service Form 1 | Service Form 2 |
miRNAOverexpression | Plasmid construction | Slow virus/adenovirus/adenovirus |
miRNAinterfere | Plasmid construction | Slow virus/adenovirus/adenovirus |
lncRNAOverexpression | Plasmid construction | Slow virus/adenovirus/adenovirus |
lncRNAinterfere | Plasmid construction | Slow virus/adenovirus/adenovirus |
lncRNAKnock out | Plasmid construction | Slow virus/adenovirus/adenovirus |
circRNAOverexpression | Plasmid construction | Slow virus/adenovirus/adenovirus |
circRNAinterfere | Plasmid construction | Slow virus/adenovirus/adenovirus |
circRNAKnock out | Plasmid construction | Slow virus/adenovirus/adenovirus |
Dual luciferase assay | Plasmid construction | Complete outsourcing services |






 Back
Back





















