Original link:Heterobiosis - luciferase reporter gene detection
Heterobiosis luciferase reporter gene detection is an ideal reporter gene because mammalian cells do not contain endogenous luciferase, which immediately generates functional luciferase once transcription is complete. Single reporter gene experiments are often influenced by various experimental conditions, while dual reporter genes provide a baseline for the experiment through co transfected "controls" as internal references, which can minimize the impact of external factors such as cell activity and transfection efficiency on the experiment, making the data results more reliable. The Dual Luciferase ® reporter gene detection system expresses both firefly luciferase and sea kidney luciferase in cells simultaneously, without homology and corresponding to different reaction substrates, therefore there is no cross interference. Thanks to the super strong optical signal and ultra-high signal-to-noise ratio.
MiRNA target gene validation
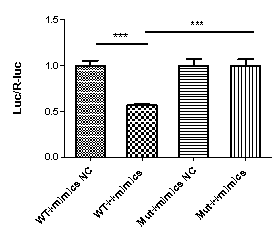
MiRNA mainly acts on the 3 'UTR of the target gene (degrading or inhibiting translation). The 3' UTR (wild-type and binding site mutant) sequence of the target gene is constructed into the 3 'end of the reporter gene F-Luc in the vector. By comparing the changes in reporter gene expression (decreased or unchanged luciferase activity) after overexpression of miRNA, the site of action between miRNA and the 3' UTR of the target gene is determined.
Objective: To verify whether miRNA has a regulatory effect on the target gene 3'UTR.
Material: Plasmid pMIR-REPORT Luciferase gene 3'UTR (Wt); PMIR-REPORT Luciferase gene 3'UTR (Mut); PRL CMV (H321, Promega); 293T cell line
Step: Target prediction - Construct plasmid - Transfect cell detection - Report gene detection (Luciferase activity detection) - Statistical analysis
Result display:
Study on promoter activity
Transcription factors are protein molecules with special structures that regulate gene expression, also known as trans acting factors. Some transcription factors only bind to specific sequences in their target promoters, which are called cis factors. The DNA binding domain of transcription factors covalently binds to cis factors, thereby inhibiting or enhancing gene expression.
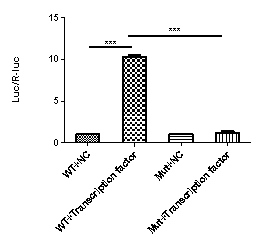
Transcription factors mainly act on the promoter of target genes by replacing the promoter region sequence of the target gene with the promoter of the reporter gene F-Luc. By co expressing transcription factors, changes in the expression of the reporter gene are determined to identify the binding site between transcription factors and target gene promoters, as well as their effects on the target gene.
Purpose: To investigate the effect of transcription factors on the promoter activity of target genes
Materials: Experimental plasmid (pGL4.10 gene promoter); Control plasmid; PRL CMV (E2261, Promega); transcription factor plasmid; 293T cell line
Step: Target prediction - Construct plasmid - Transfect cell detection - Report gene detection (Luciferase activity detection) - Statistical analysis
Result display:
The customer needs to provide information:
1. Target gene name
2 target gene species
3 names of regulatory factors (miRNA or transcription factors)
Provide to customers:
1. Prediction results of binding sites
2 Plasmids and Their Construction Report
3 Double Fluorescent Enzyme Detection Reports






 Back
Back





















