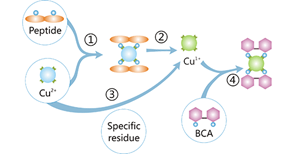
Principle, experimental steps, and precautions for measuring protein concentration using BCA method
Protein concentration determination is an important method for calculating the recovery rate of purification methods. Common measurement methods include biuret method, Lowry method, UV absorption method, BCA protein concentration detection method, etc. The most commonly used method is the BCA method (dioctyl acid method or diquinolinecarboxylic acid method). The full name of BCA is Bicinchonic Acid Assay, also known as Smith Assay, which was invented by Paul K. Smith. This method determines the concentration of proteins by displaying the color changes of samples with different concentrations.
Detection principle
BCA is an alkaline water-soluble complex with stable properties. In the alkaline environment provided, proteins can reduce Cu2+in BCA reagents to Cu+, which then chelates with BCA reagents to form a blue purple complex with a strong absorption peak at 562nm wavelength. The protein concentration can be determined by measuring the absorbance and combining it with the standard curve. The BCA method has been widely used due to its strong anti-interference ability, simplicity, accuracy, and high sensitivity, but it is also susceptible to temperature and incubation time.
Experimental steps
1、 Prepare standard products and working fluids
1. Prepare BSA standard system (two preparation methods for the linear range of 20-2000 μ g/mL or 5-250 μ g/mL standard, please choose the appropriate method according to your habits). [Note]: The concentration of BSA standard is 2 mg/mL, and the diluent is a solution of the protein sample. In principle, the protein should be dissolved
In what solution is the white sample in, and what solution should be used to dilute the standard. But it can also be diluted with water or 1 X PBS. BSA Standard System Preparation Table (After preparation, it can be placed in a refrigerator at 4 ℃ for multiple uses)
2. Prepare BCA working fluid
① Calculate the total volume of BCA working fluid required. Total BCA working fluid volume=(number of standard samples+number of test samples) x number of repetitions x each
BCA working fluid required for the sample. [Note]: During the test tube method, 2.0 mL of BCA working solution is added to each sample, and each sample is tested using a microplate
Add 200 μ L BCA working solution to the sample.
② Preparation of BCA working solution: Add 1 volume of BCA reagent B (A: B=50:1) to 50 volumes of BCA reagent A and mix thoroughly. 【 Note 】: BCA working fluid is placed in a sealed container and stabilized at room temperature for 24 hours.
2、 Testing method
1. Test tube testing method (sample: BCA working solution=1:20)

2. Microplate detection method (sample: BCA working solution=1:20)
① Take 10 μ L of standard and test samples each and add them to the microplate. [Note]: The ratio of sample to working solution is 1:20, and the detection range is 125-2000 μ g/mL. If the sample concentration is very low, 25 μ L of standard substance and the sample to be tested can be used for detection (i.e. 1:8). At this time, the detection of the reagent kit
The measurement range is 20-2000 μ g/mL.
② Add 200 μ L of BCA working solution to each well and mix thoroughly by blowing with the gun tip. Cover the microplate and incubate at 37 ℃ for 30 minutes.
③ Cool to room temperature and measure absorbance at a wavelength range of 562 nm on an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) reader.
④ Draw a standard curve (X-protein concentration) based on the absorbance of BSA standard (subtracting the OD value of the blank well in the standard to obtain the final reading)
Degree μ g/mL; Y-final OD 562nm). Calculate the protein concentration of the sample based on the standard curve and the dilution factor of the sample.
matters needing attention
Accuracy and reliability are crucial in the experimental process of detecting protein concentration using BCA method. Here are some key operational points and common problems that may be encountered during the experimental process, as well as their solutions:
▶ Preparation and storage of reagents: Ensure that all reagents are thoroughly mixed before use and stored at the recommended temperature. The freshness of reagents has a significant impact on experimental results, and expired or improperly stored reagents may lead to inaccurate results.
▶ Strict adherence to the sequence of operations: When conducting BCA experiments, strictly follow the order of reagent addition and operational steps to avoid any reversal or omission of steps. The order of these steps is designed to maximize reaction efficiency and consistency of results.














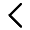 Back
Back
 Back
Back