Experimental dry goods | Techniques of BCA method for protein concentration determination
BCA method is an improved method of Lowry method. Compared with the Lowery method, the BCA method is simpler and more convenient to operate, with better stability of its reagents and formed color complexes, almost unaffected by other interferences, and high sensitivity (micro detection can reach 0.5ug/ml), making it more flexible to apply. The significant advantage of BCA method compared to Bradford method is that it is not affected by detergents (SDS, Triton X-100, Tween-20, etc.).
The principle of BCA method experiment
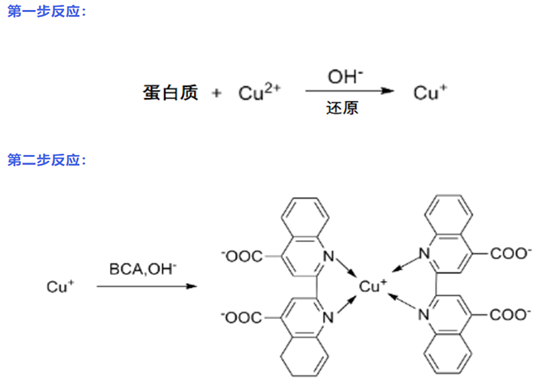
BCA is a stable alkaline water-soluble complex. Under alkaline conditions, proteins reduce Cu2+to Cu+, which interacts with the unique BCA reagent A (containing BCA) to produce a sensitive color reaction, forming a purple complex. The water-soluble complex exhibits strong absorbance at A562 nm, and there is a good linear relationship between absorbance and protein concentration over a wide range. The protein concentration can be calculated based on the absorbance value.
BCA experimental materials and equipment
✔ Material List
1. BCA reagent kit: usually contains BCA solution A and B, which need to be mixed evenly according to the specified ratio before use.
2. Protein standard: Generally, bovine serum albumin (BSA) is used as the standard protein to draw the standard curve.
3. Colorimetric dish: 96 well plate or other specifications can be used to hold samples and perform photometric measurements.
4. Centrifugal tube: used for sample preparation and storage.
5. Pipette and matching suction head: used for precise measurement and addition of liquids of different volumes.
6. Deionized water: used for preparing solutions and diluting samples
✔ Equipment Introduction
Spectrophotometer: In the process of determining protein concentration using BCA method, a spectrophotometer is an indispensable instrument used to measure the absorbance of a sample at a specific wavelength (562 nanometers). When choosing a spectral photometer, the following points should be considered:
Accuracy: The instrument must be able to accurately read changes up to 0.001 absorbance units.
• Wavelength range: Ensure that the device can cover the required testing wavelengths, especially the 562 nanometers required for BCA method.
• Processing capability: Select a photometer with appropriate reading speed and sample processing capability based on the experimental scale, such as a single well to porous plate photometer.
BCA experimental operation steps
1、 Microplate detection
① BCA working fluid preparation. According to the standard and sample quantity, prepare an appropriate amount of BCA working solution by adding 50 volumes of BCA reagent A to 1 volume of BCA reagent B (50:1), and mix thoroughly.
② Draw the standard curve. Take an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) plate (the bottom of the plate cannot be touched by hand, usually the side wall is taken), and add the reagents according to the data in the table below:
③ Sample preparation: Dilute the protein sample to an appropriate concentration with deionized water, take 20 ul of the sample, and add 200 ul of BCA working solution (protein solution: working solution=1:20). When adding samples, gently blow the gun and mix the liquid evenly.
④ After shaking and mixing, let it stand at 37 ℃ for 20-30 minutes. Cool to room temperature. The color change is shown in the following figure:
⑤ Measure the absorbance value at A562 nm using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) reader, with the absorbance value without BSA as the blank control.
⑥ Draw a standard curve with protein content (ug) as the horizontal axis and absorbance value as the vertical axis.
⑦ Based on the measured absorbance value, the protein content of the sample can be calculated on the standard curve.
⑧ Calculate protein concentration: Divide the obtained protein content by the sample volume of 20 ul, and then multiply by the corresponding dilution factor to obtain the actual concentration of the sample to be tested.
2、 Microplate detection
① BCA working fluid preparation. According to the standard and sample quantity, prepare an appropriate amount of BCA working solution by adding 50 volumes of BCA Reagent A to 1 volume of BCA Reagent B (50:1), and mix thoroughly.
② Select 7 clean test tubes, including 6 tubes numbered 1-6 (including the first blank tube), and the other tube labeled as the test tube. Accurately transfer the corresponding standard protein solution or test sample, distilled water, and BCA working solution into a test tube using a pipette according to the table below.
③ Take an appropriate volume of standard protein (diluted with deionized water according to the situation) and mix it evenly in a ratio of protein solution: working solution=1:20. Bath at 37 ℃ for 30 minutes. Cool to room temperature.
④ Then extract the solutions from each test tube into a colorimetric dish and measure the absorbance value using a spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 562nm.
Precautions for BCA experiment
To ensure the accuracy of protein concentration measurement, it is best to make 3 replicates and remove outliers if necessary.
The BCA method for measuring protein concentration is easily affected by time and temperature, so it is best to make a standard curve for each measurement.
When adding samples, be sure to add them accurately and avoid the formation of bubbles as much as possible to avoid affecting the measurement (after adding samples, you can use a syringe to puncture the bubbles and place the 96 well plate on a shaker to mix for a moment, so that the sample is fully in contact with the working solution).
After incubation, the absorbance should be detected as soon as possible and the detection speed should be accelerated as much as possible to avoid errors.














 Back
Back
 Back
Back