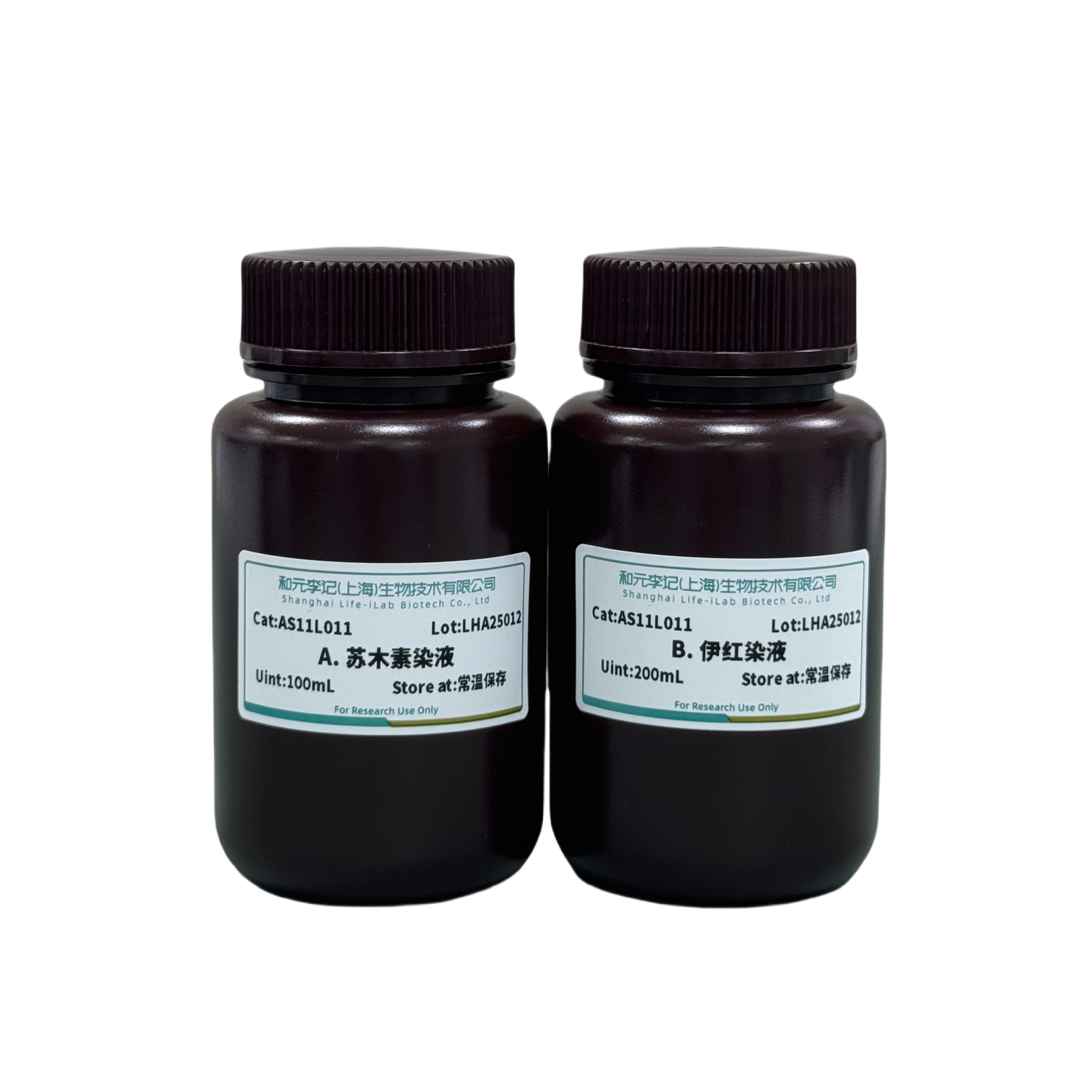
product description
The Hematoxylin and Eosin (HE) staining kit is formulated by combining multiple classic methods. This solution is mercury free and can be used for immunohistochemical counterstaining and H&E staining.
ordering information
product name | Item number | specifications |
Hematoxylin staining Solution | AS11L011 | 200mL |
Transportation and storage
Transport at room temperature. Store at room temperature and avoid light, with a shelf life of 12 months.
Usage
1. Preparation of reagents
Acid alcohol: Add 1mL hydrochloric acid to 100mL of 70% ethanol and store at room temperature. Note: After frozen sectioning, various steps (drying, fixation with ethanol or methanol, thermal fixation, using charged or sticky caps) are taken to ensure that the tissue sections do not detach during the staining process.
2. 95% ethanol: Before HE staining begins, tissue sections need to be fixed and hydrated. Place the slices in 95% ethanol for about 2 minutes, start hydration and fix the tissue. Note: Skipping the hydration and fixation of tissues with 95% ethanol does not affect the morphological details.
3. Hydration: Further hydrate the tissue sections for 3-5 minutes and wash away any residual ethanol from the previous step.
4. Hematoxylin: After hydration, tissue sections are stained with hematoxylin for 1-3 minutes, and the staining time can be adjusted according to the staining results and requirements. Hematoxylin is a basic dye that can stain acidic components of cells, including nucleic acids, mucopolysaccharides, and acidic glycoproteins, staining them blue or blue purple. Note: Without hematoxylin, the Yihong Society will dye the tissue bright pink; It is obvious that there is a lack of cell nucleus. The organizational structure is difficult to distinguish, and the intracellular components are almost non-existent, making it difficult to distinguish. To address the above issues, hematoxylin can be used for counterstaining.
(1) Weak staining is due to poor self dissolution or fixation; Excessive decalcification; Insufficient staining time; Excessive decolorization (excessive ratio of acid to alcohol or prolonged decolorization time of acid ethanol); The effect of hematoxylin is weak (due to excessive oxidation (aging) or water dilution); Contamination of rinsing solution; Slicing too thin; Insufficient removal of ethanol or rinsing with water before staining.
(2) Excessive staining is due to: dry tissue sections; Excessive concentration of hematoxylin; The dyeing time is too long; Excessive adhesive on glass slides; Weak decolorization or insufficient time; Slice too thick; The duration of heat exposure is too long.
5. Water washing: After staining with hematoxylin, it is very important to wash the tissue with water. This step and subsequent washing can remove excess dyes, mordants, etc. Appropriate rinsing can remove the surface metallic luster, which can prevent the staining of hematoxylin. Note: Skipping this step will result in adverse outcomes such as precipitation formation, dilution of dye solution, and the presence of surface metallic luster.
6. Acid alcohol: Acid alcohol color separation agent for 3-5 seconds. In the hematoxylin staining method, tissue sections are intentionally over stained, and acid alcohol will remove excess dye and background staining on the glass slide.
Note: If this step is omitted, the slice will appear dark purple, and eosinophilic structures (such as collagen) will not appear bright pink, making it difficult to distinguish between tissue structures and affecting accurate judgment of the slice. Additionally, excessive color separation may be due to: high acid concentration; The decolorization time is too long, etc. Insufficient color separation is due to: low acid concentration; Insufficient decolorization time; There is excess protein or gelatin on the slice.
7. Water washing: Wash for 30 seconds to terminate the acid alcohol reaction and further prevent acid alcohol from removing a large amount of hematoxylin from tissue slices. Note: If the slices have not been rinsed, acid alcohol can cause excessive decolorization. If the decolorizing agent is not removed, acid alcohol will continue to remove hematoxylin from tissue slices.
8. Rinse with tap water or blue with a blue solution: Rinse with tap water for 3-5 minutes to achieve bluing treatment, converting the purple red hematoxylin into blue purple. Usually, the blue reagent is pH dependent and consists of an alkaline solution. Therefore, if tap water is used as a blue reagent, daily monitoring of pH value is very important because the pH value of tap water may fluctuate every day. Or use a blueing solution for 30 seconds to 1 minute; Rinse with flowing tap water for 5 minutes; Note: Skipping the blueing reagent step will result in subtle changes in the color of the hematoxylin dye solution, making it difficult to distinguish. Instead of dark blue, the nucleus will appear purple, sometimes even red. The nucleus should not be excessively blue stained. If the tissue is stained too blue, it is usually caused by excessive hematoxylin on the tissue section.
9. Water washing: Prepare for eosin counterstaining by washing for 30 seconds to remove excess blueing reagent. Because in alkaline environments, eosin cannot be dyed. Removing the blue reagent with water washing will allow eosin to maintain its acidic pH value, allowing it to be uniformly counterstained. Note: After using the blue reagent, tissue sections cannot be stained correctly with eosin without washing with water. Therefore, acidic structures will be stained pale and uneven, leading to erroneous judgments.
10. Eosin: In order to correctly distinguish intracellular structures, Eosin is an excellent counterstain for hematoxylin. Eosin counterstain for 30-60 seconds, and the staining time can be adjusted according to the staining results and requirements. Eosin is an acidic dye that can stain the cytoplasm, especially mitochondria, secretory granules, and collagen. It can distinguish different organelles and connective tissues within cells. Note: Failure to use eosin counterstain tissue sections will result in low differentiation of tissue sections.
(1) The weak staining is due to: thin tissue slices; Insufficient staining time; Subsequently, 95% alcohol undergoes excessive differentiation.
(2) Excessive staining is due to: high concentration of dye solution (possibly due to excessive evaporation); The tissue slice is too thick; The dyeing time is too long; Subsequently, 95% alcohol did not differentiate properly.
(3) The undifferentiated (one color) of eosin staining is due to incomplete fixation; Excessive staining (dyeing time too long or dye concentration too high).
11. 95% ethanol: Treat with 95% ethanol for 2 seconds to 1 minute, and adjust according to the staining results and requirements; The differentiation of eosin will produce different shades of pink. Note: If 95% ethanol is diluted (e.g. carrying eosin from the previous staining step), the differentiation effect is poor.
12. 100% ethanol: decolorize tissue sections using 100% ethanol. 100% ethanol treatment for 1 minute; Treat with new 100% ethanol for 1 minute. Note: This step is difficult to notice, as without 95% ethanol, it is difficult to distinguish acidic structures and tissue slices turn pink. Without 100% ethanol dehydration, tissue slices cannot be completely dehydrated, resulting in the formation of water droplets under the cover. These water droplets can combine with the next step of xylene to form a white turbidity, which will affect the quality of tissue sections.
13. Xylene: Xylene treatment for 5 minutes. After sufficient dehydration, xylene can remove alcohol from tissue slices. After removing alcohol, xylene can also be used as an embedding agent to ensure solubility when adding a cover slip on a glass slide. Due to potential toxicity, xylene alternatives such as limonene and cycloalkanes can also be used. Substitutes can provide the same tissue staining quality, and they are safer to use and easier to operate. Note: When skipping this step, if xylene transparency is not used, alcohol will be stored on the tissue slices, causing eosin to flow out of the slices.
14. Sealing: Neutral gum sealing, naturally air dried or baked, observed under a microscope.
Staining result: The nucleus is stained blue; The cytoplasm is stained red.
matters needing attention
1. This product is only for scientific experimental research and should not be used in clinical diagnosis, treatment, or other fields.
2. For your safety and health, please wear lab clothes and disposable gloves when operating.
3. Reagents should be stored in a cool, dry, and well ventilated environment.
4. It is recommended to take 1-2 samples for preliminary experiments when using this kit for the first time.
Related product recommendations
Universal tissue cell fixative (4% paraformaldehyde) (item number: AC28L112)
Anti fluorescence quencher (item number: AC28L512)
Hematoxylin staining solution (item number: AS11L021)
Eosin staining solution (item number: AS11L031)
This product is only for scientific experimental research and should not be used in clinical diagnosis, treatment, or other fields.














 Back
Back
 Back
Back